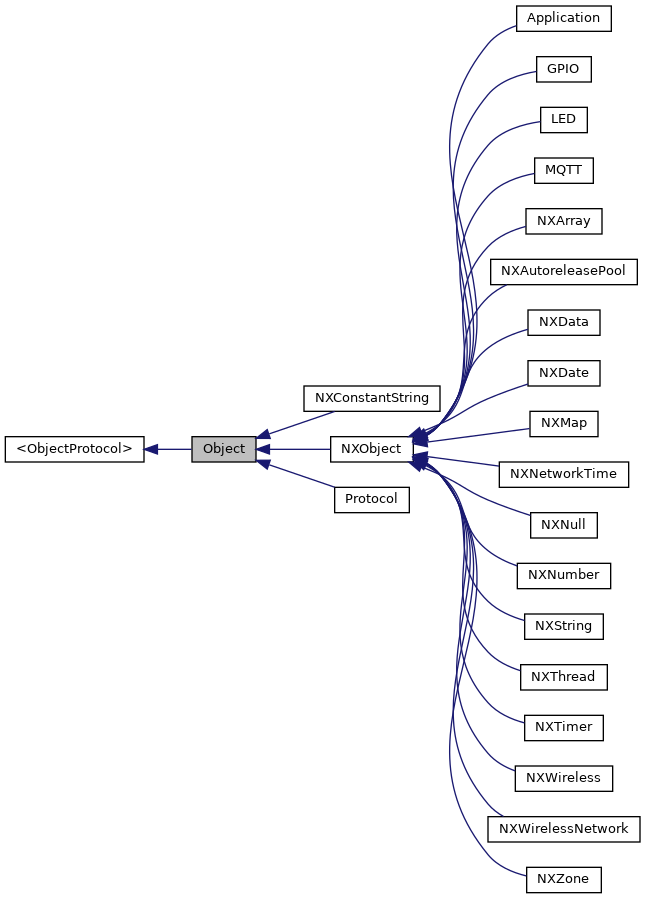
The root class of all Objective-C classes. More...
#import <objc/objc.h>
Instance Methods | |
| (void) | - dealloc |
| Free resources for an existing instance. | |
| (id) | - init |
| Initialize the instance, after allocation. More... | |
| (Class) | - class |
| Returns the class of the instance. More... | |
| (Class) | - superclass |
| Returns the superclass of the instance. More... | |
| (BOOL) | - isEqual: |
| Compares the receiver to another object for equality. More... | |
| (BOOL) | - isKindOfClass: |
| Returns a Boolean value that indicates whether the receiver is an instance of a given class. More... | |
| (BOOL) | - conformsTo: |
| Checks if the receiver's class conforms to a protocol. More... | |
| (NXString *) | - description |
| Returns a string that represents the instance. More... | |
 Instance Methods inherited from <ObjectProtocol> Instance Methods inherited from <ObjectProtocol> | |
| (BOOL) | - respondsToSelector: |
| Checks if the receiver responds to a selector. More... | |
Class Methods | |
| (void) | + initialize |
| Performs one-time initialization for the class. More... | |
| (id) | + alloc |
| Allocate a new class instance. More... | |
| (Class) | + class |
| Returns the class object. More... | |
| (Class) | + superclass |
| Returns the superclass of the class. More... | |
| (const char *) | + name |
| Returns the name of the class. More... | |
| (BOOL) | + conformsTo: |
| Checks if the class conforms to a protocol. More... | |
| (NXString *) | + description |
| Returns a string that represents the class. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| Class | isa |
| A pointer to the object's class structure. More... | |
Detailed Description
The root class of all Objective-C classes.
This class is the base class for all objects in Objective-C. It provides basic memory management and introspection capabilities.
Method Documentation
◆ alloc()
| + (id) alloc |
Allocate a new class instance.
- Returns
- A pointer to the instance, or nil if the allocation failed.
◆ class() [1/2]
| - (Class) class |
Returns the class of the instance.
- Returns
- The class of the receiver.
◆ class() [2/2]
| + (Class) class |
Returns the class object.
- Returns
- The class object for the receiver.
◆ conformsTo:() [1/2]
Checks if the class conforms to a protocol.
- Parameters
-
aProtocolObject The protocol to check conformance against.
- Returns
- YES if the class conforms to the specified protocol, NO otherwise.
This class method determines whether the receiving class adopts or inherits from the specified protocol. A class conforms to a protocol if it explicitly declares that it adopts the protocol, or if it inherits from a class that conforms to the protocol.
Reimplemented from <ObjectProtocol>.
Implemented in Protocol.
◆ conformsTo:() [2/2]
Checks if the receiver's class conforms to a protocol.
- Parameters
-
aProtocolObject The protocol to check conformance against.
- Returns
- YES if the receiver's class conforms to the specified protocol, NO otherwise.
This instance method determines whether the receiving object's class adopts or inherits from the specified protocol. This is equivalent to calling the class method on the receiver's class.
Reimplemented from <ObjectProtocol>.
Implemented in Protocol.
◆ description() [1/2]
| + (NXString *) description |
Returns a string that represents the class.
- Returns
- A string that describes the receiver.
Provided by category Object(Description).
◆ description() [2/2]
| - (NXString *) description |
Returns a string that represents the instance.
- Returns
- A string that describes the receiver.
Provided by category Object(Description).
◆ init()
| - (id) init |
Initialize the instance, after allocation.
- Returns
- The initialized object.
Subclasses should override this method to perform custom initialization, and free resources if the initialization fails.
◆ initialize()
| + (void) initialize |
Performs one-time initialization for the class.
This method is called automatically by the Objective-C runtime before the class receives messages.
Subclasses may override this method to perform initialization tasks like setting up class variables or initializing static data structures. If subclasses implement this method, they are called first, and may be called multiple times.
◆ isEqual:()
Compares the receiver to another object for equality.
- Parameters
-
anObject The object to compare with the receiver.
- Returns
- YES if the objects are equal, otherwise NO.
When comparing two objects, this method should be overridden to compare the contents of the objects.
Reimplemented from <ObjectProtocol>.
◆ isKindOfClass:()
Returns a Boolean value that indicates whether the receiver is an instance of a given class.
- Parameters
-
cls A class object.
- Returns
- YES if the receiver is an instance of cls or an instance of any class that inherits from cls, otherwise NO.
Reimplemented from <ObjectProtocol>.
◆ name()
| + (const char *) name |
Returns the name of the class.
- Returns
- A C-string containing the name of the class.
Reimplemented from <ObjectProtocol>.
Implemented in Protocol.
◆ superclass() [1/2]
| - (Class) superclass |
Returns the superclass of the instance.
- Returns
- The superclass of the receiver, or Nil if it is a root class.
◆ superclass() [2/2]
| + (Class) superclass |
Returns the superclass of the class.
- Returns
- The superclass of the receiver, or Nil if it is a root class.
Field Documentation
◆ isa
|
protected |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- include/runtime-gcc/objc/Object.h